In today’s digital transformation era, AI agents and APIs are reshaping how businesses automate
workflows. By combining the autonomous decision-making of AI agents with the connective
power of APIs, organizations can streamline processes, reduce manual work, and enable
intelligent, adaptive operations.
In this article we will present and explain the implementation steps of how we at Ähdus
Technology are integrating agenting AI solutions within API workflows for some of our AI based
projects. In today’s time, every scaled product must be dealing with API driven product
development and this might be helpful for your software and AI teams to combine best strategies
together based on our experiences.
What are AI Agents?
Before we explore API workflows, let us first look into AI agents. AI agents are autonomous
software systems capable of perceiving their environment, reasoning, and taking actions without
continuous human input. They use techniques such as machine learning and natural language
processing (NLP) to interpret data, execute multi-step tasks, and learn from feedback. The future
belongs to AI Agents, every product will be having AI Agents, sooner or later.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents
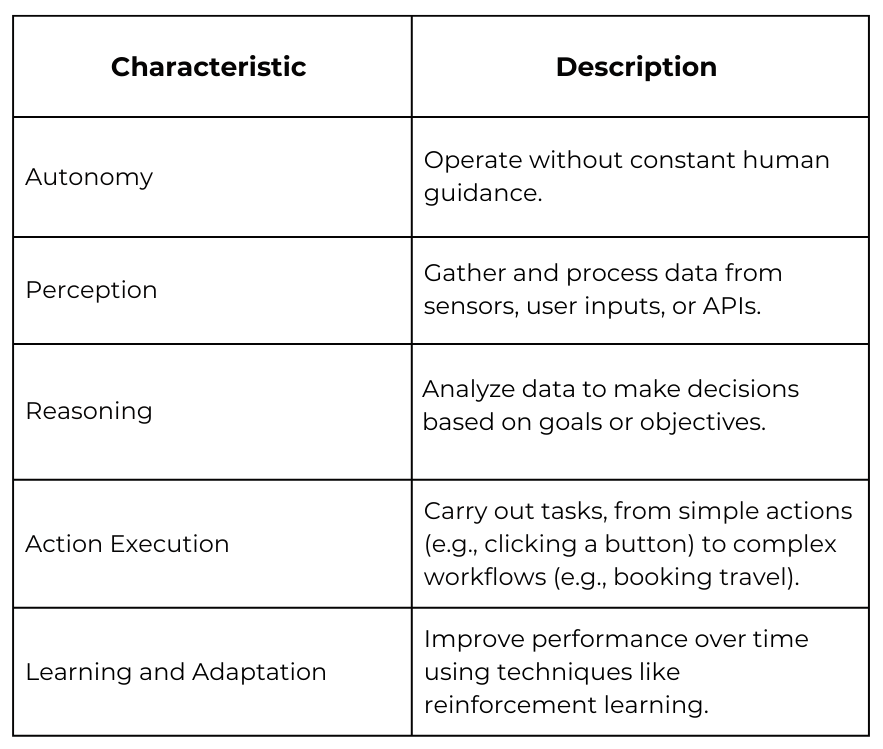
Types of AI Agents
AI agents vary in complexity and functionality. Here’s a simplified classification:
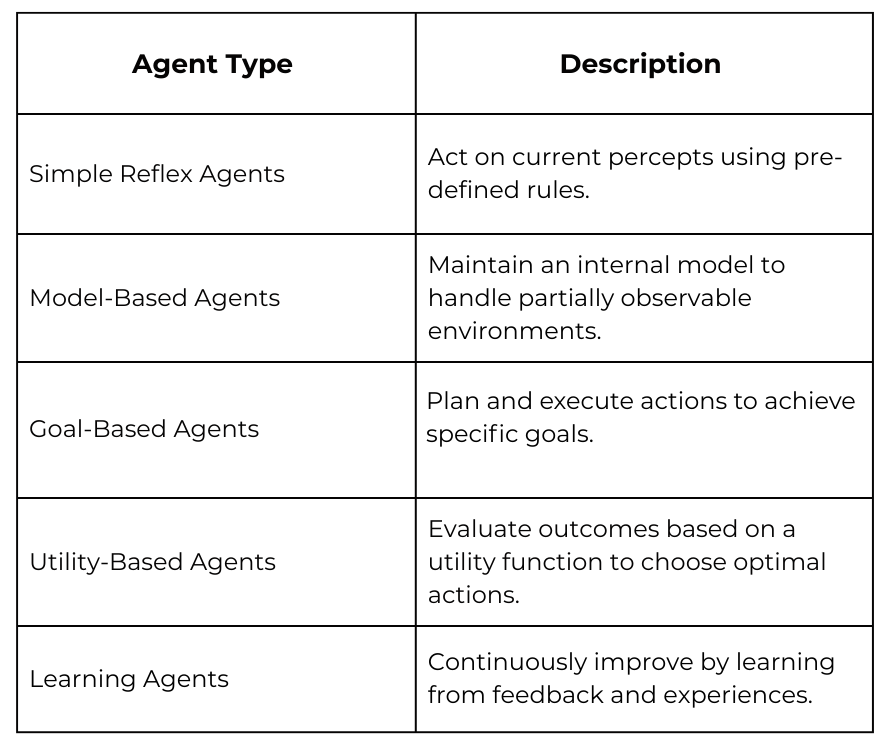
Role of APIs in Automation
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of digital connectivity. They allow
different software systems to communicate, enabling automation across multiple platforms. In the
context of AI agents, APIs serve two critical functions:
- Data Ingestion: AI agents rely on real-time data from various systems; databases, CRMs,
social media, IoT devices; which is provided via APIs. - Action Execution: Once an AI agent decides on an action, APIs allow it to interact with
external systems (e.g., updating records, triggering workflows, or processing
transactions).
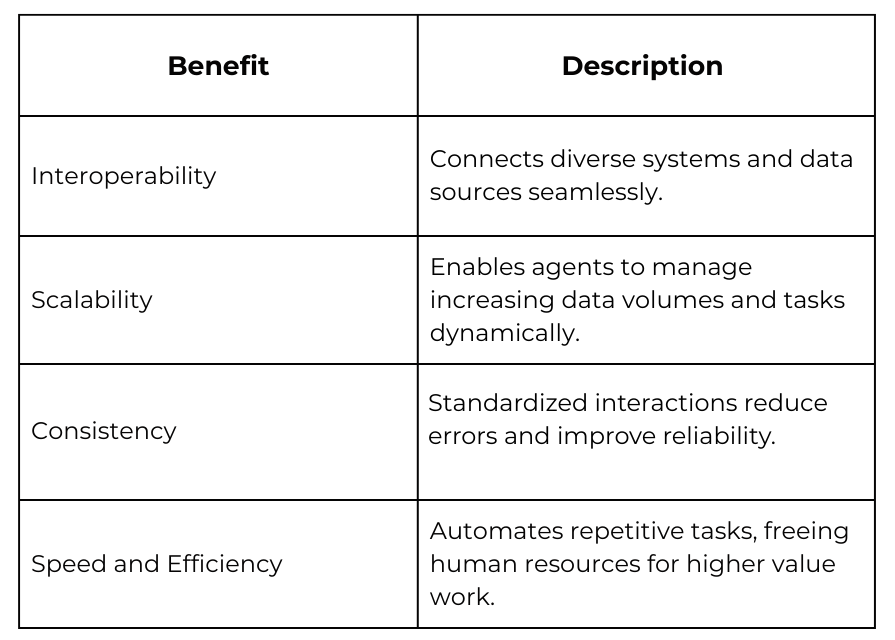
Benefits of API-Driven Automation
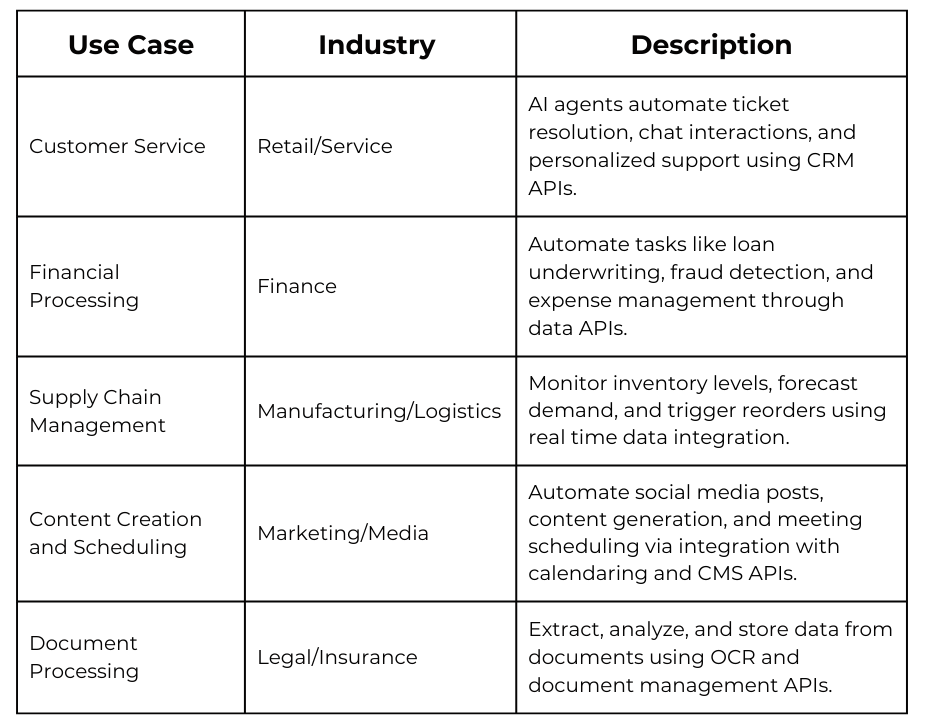
Common Use Cases
AI agents integrated with APIs have wide-ranging applications. Here are some prominent use
cases:
Architecture Breakdown
Integrating AI agents with API workflows involves several layers; from data ingestion to
decision making and action execution. Below is a conceptual breakdown of the architecture.
Core Components
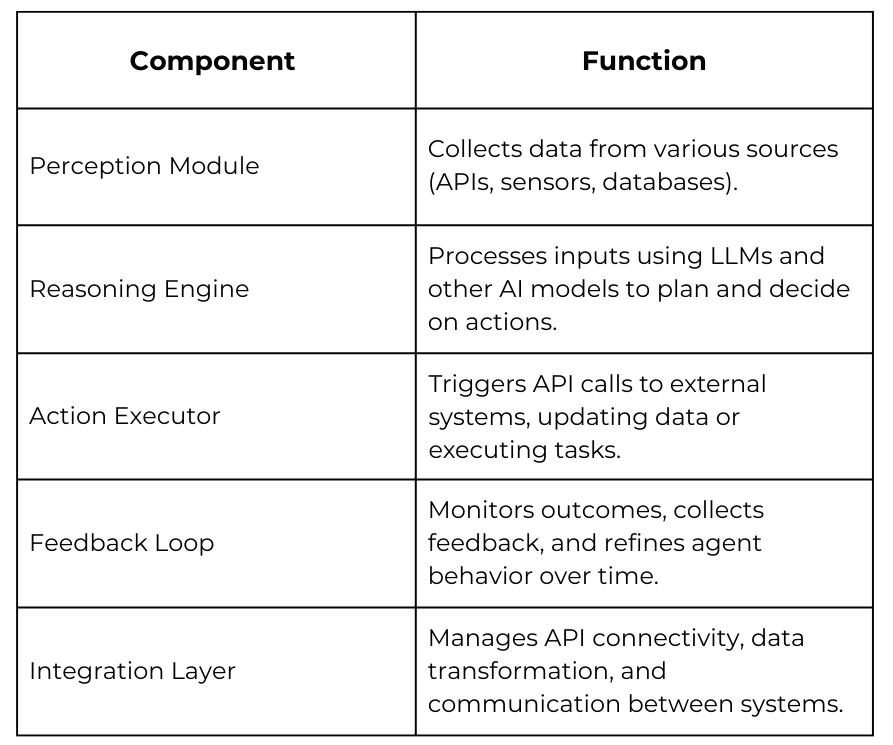
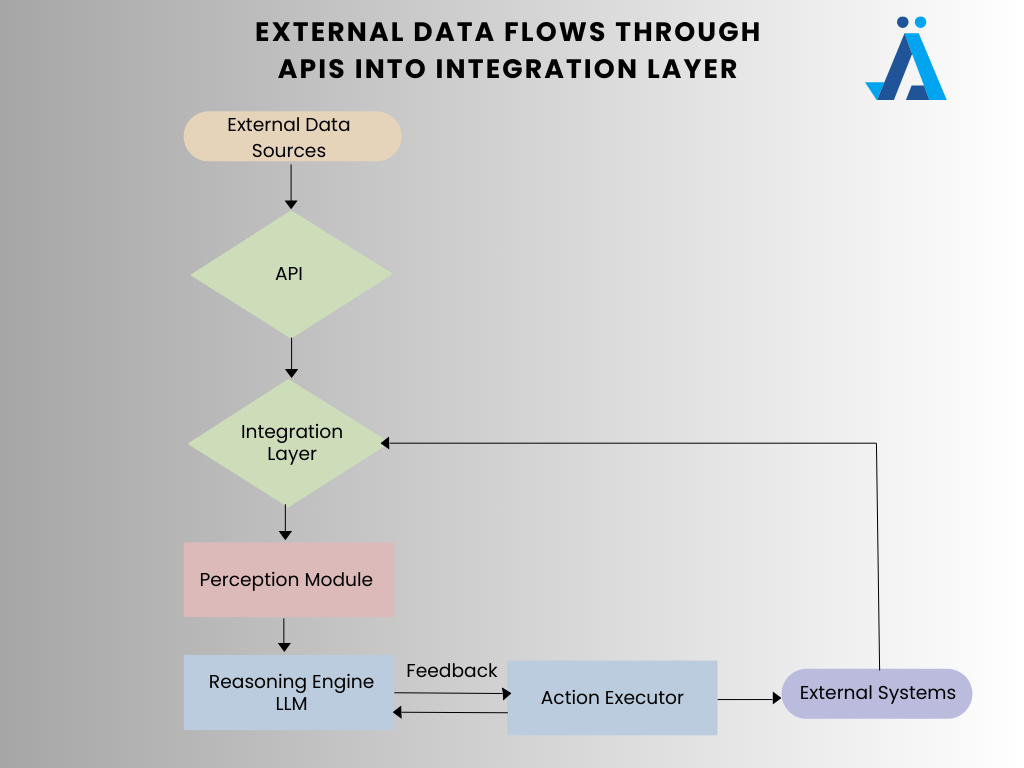
processed by the perception module and reasoning engine, then executed via API calls by the
action executor. Feedback loops help refine agent decisions.
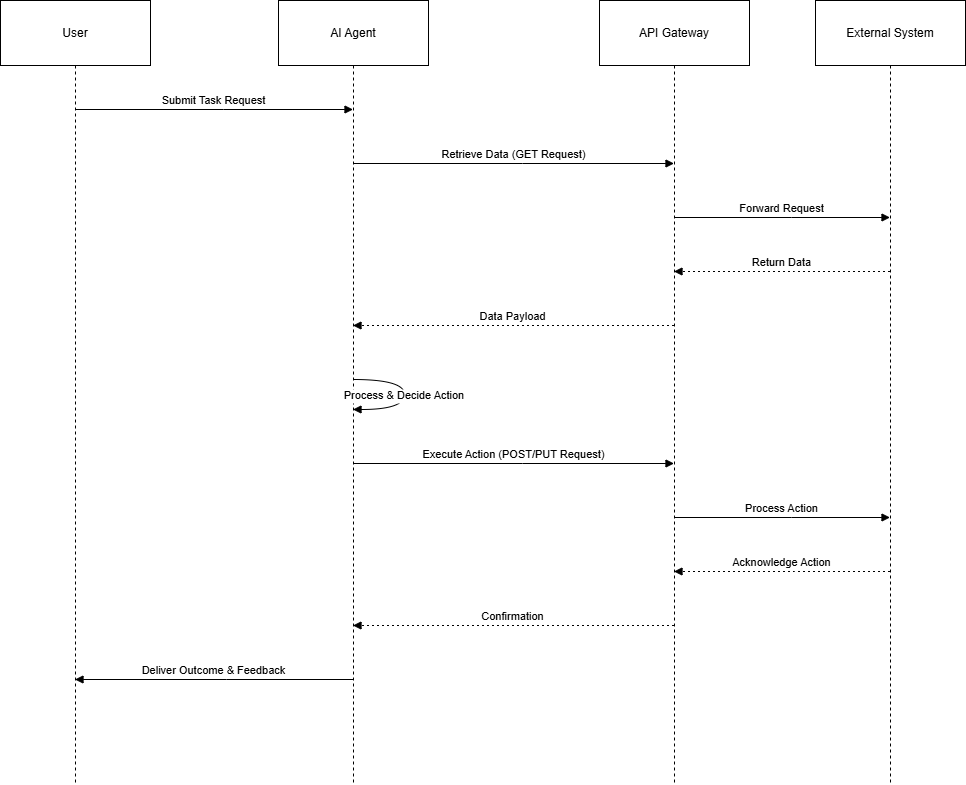
data via APIs, makes decisions, and executes an action through external systems.
Conclusion
Integrating AI agents with API workflows creates a powerful synergy that automates complex
tasks by combining intelligent decision-making with robust data connectivity. The layered
architecture; from perception to execution, ensures that AI agents can dynamically interact with
their environment, process data, and execute actions autonomously. As businesses continue to
adopt these technologies, the role of APIs in bridging systems and enabling scalable automation
will become even more critical.
This fusion of AI and API-driven automation not only drives efficiency and innovation but also
opens up new possibilities for transforming business processes across various industries.




